Diagnosing Gallstones
Ultrasound of the liver for diagnosing gallstones
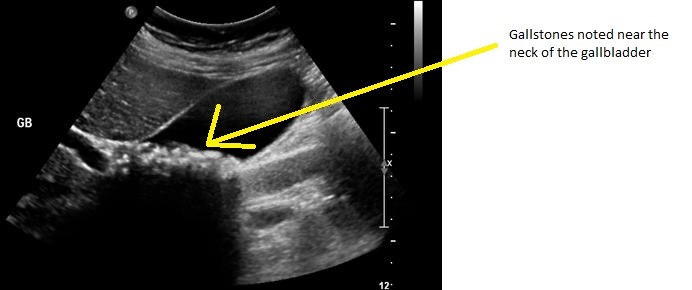
The gallbladder is situated on the right upper part of the abdomen. The function of the gallbladder is to store a fluid called bile which is released into the small intestines during digestion of fats.
One of the common problems that could develop in the gallbladder are gallstones. Gallstones are stones made usually of cholesterol.
Symptoms
If a gallstone or gallstones get trapped in the duct (opening of that gallbladder) it might cause symptoms such as nausea and vomiting, intense pain on the upper right side of the abdomen, pain in the right shoulder and back pain between the shoulder blades.
Preparation
A liver ultrasound scan also known as a general or abdominal scan is requested by your Doctor. Before the scan you will be required to fast for at least 8-12 hours before the scan. This allows for the bile to build up in the gallbladder making it easy to visualise. Fasting also reduces the bowel gas in the abdomen to allow for easy visibility of the organs. If you are diabetic you could arrange to have a morning appointment to avoid fasting during the day.
The ultrasound examination
During the scan other organs such as pancreas, abdominal aorta, liver, biliary ducts, kidneys, spleen as well as the gallbladder will be assessed. The scan involves using an ultrasound probe or camera to view the abdominal organs. You are required to lie on your back. Ultrasound gel is then applied on the abdomen which acts as a window for the abdominal organs to be seen. The ultrasound probe or camera is moved across the abdomen whilst images will be recorded. You may be required to lie or sit in different positions to allow for easy access to all organs. You might also be asked to hold your breath to avoid acquiring blurry images and to get to some organs in the abdomen. The scan is usually less than 20 minutes.
After the scan the gel is wiped off and Sonographer practitioner will report findings to the referring Doctor. The referring Doctor will advise you if there is any specialist referral needed.





